background elimination
Data augmentation to increase performance
SOLO v1(Single Stage Instance Segmentation)
Paper Implementation
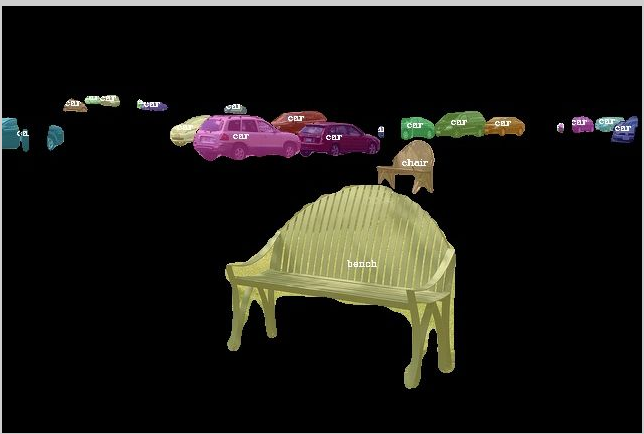



Figure 1. On the left, Original image. Middle, Image with one-shot instance segmentation. Right, image with data augmentation from my code.
-
Two stage vs Single stage
- Two stage (Doing segmentation and instance segmentation after finding the bounding box)
- Detection - Faster RCNN
- Segementation - Mask RCNN
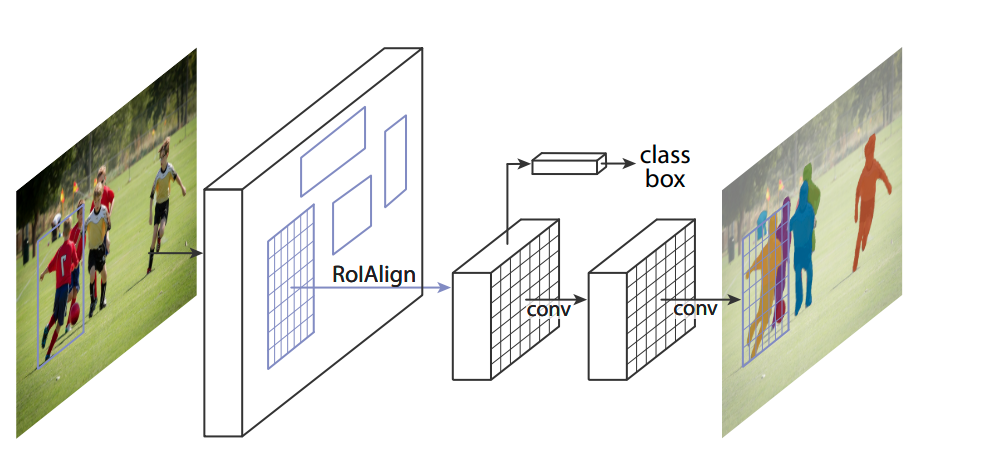
Figure 2. The Mask R-CNN framework for instance segmentation.
- One stage (Getting the instance mask right away, instead of finding the bounding box)
- Detection - YOLO
- Segmentation - SOLO
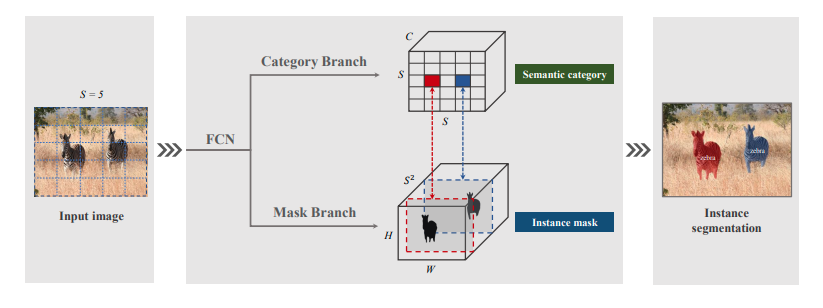
Figure 3. Solo framework
- Top-down segmentation
- It is greatly affected by the performance of the bounding box because it is first detected and then segmented.
- e.g. Mask R-CNN
- Bottom-up segmentation
- there is a pixel-embedding method to be greatly influenced by the grouping.
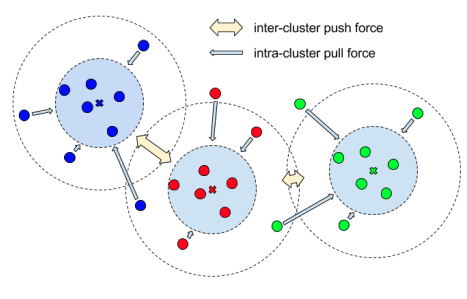
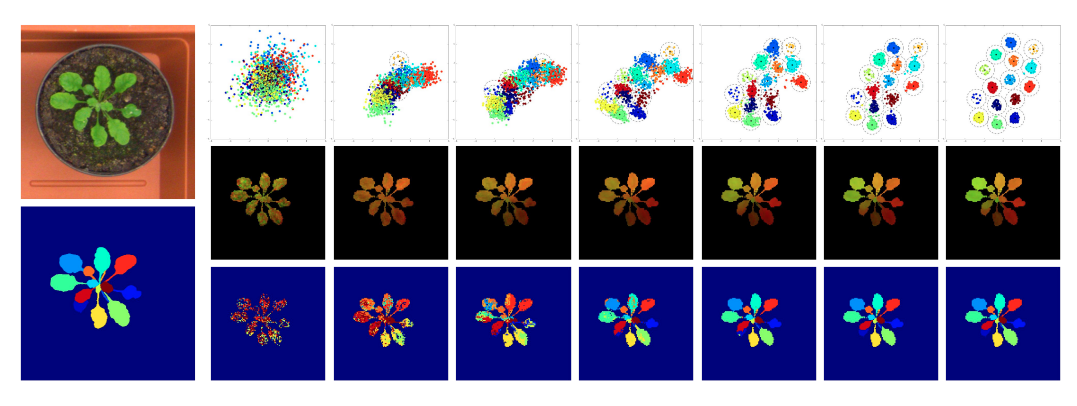
Figure 4. Bottom-up segmentation (Pixel-wise embedding)
Modifiying Solo code
def show_result_ins(img,
result,
class_names,
score_thr=0.3,
sort_by_density=False,
out_file=None):
"""Visualize the instance segmentation results on the image.
Args:
img (str or np.ndarray): Image filename or loaded image.
result (tuple[list] or list): The instance segmentation result.
class_names (list[str] or tuple[str]): A list of class names.
score_thr (float): The threshold to visualize the masks.
sort_by_density (bool): sort the masks by their density.
out_file (str, optional): If specified, the visualization result will
be written to the out file instead of shown in a window.
Returns:
np.ndarray or None: If neither `show` nor `out_file` is specified, the
visualized image is returned, otherwise None is returned.
"""
assert isinstance(class_names, (tuple, list))
img = mmcv.imread(img)
img_show = img.copy()
h, w, _ = img.shape
cur_result = result[0]
seg_label = cur_result[0] #
seg_label = seg_label.cpu().numpy().astype(np.uint8)
cate_label = cur_result[1] #ex.(9,426,640) the number of mask is 9
cate_label = cate_label.cpu().numpy()
score = cur_result[2].cpu().numpy()
vis_inds = score > score_thr
seg_label = seg_label[vis_inds]
num_mask = seg_label.shape[0] # the number of mask
cate_label = cate_label[vis_inds]
cate_score = score[vis_inds]
if sort_by_density:
mask_density = []
for idx in range(num_mask):
cur_mask = seg_label[idx, :, :]
cur_mask = mmcv.imresize(cur_mask, (w, h))
cur_mask = (cur_mask > 0.5).astype(np.int32)
mask_density.append(cur_mask.sum())
orders = np.argsort(mask_density)
seg_label = seg_label[orders]
cate_label = cate_label[orders]
cate_score = cate_score[orders]
np.random.seed(42)
color_masks = [
np.random.randint(0, 256, (1, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
for _ in range(num_mask)
]
for idx in range(num_mask):
idx = -(idx+1)
cur_mask = seg_label[idx, :, :]
cur_mask = mmcv.imresize(cur_mask, (w, h))
cur_mask = (cur_mask > 0.5).astype(np.uint8)
if cur_mask.sum() == 0:
continue
color_mask = color_masks[idx]
cur_mask_bool = cur_mask.astype(np.bool)
img_show[cur_mask_bool] = img[cur_mask_bool]*0.5+ color_mask * 0.5 #instance segmentation -> colorizing
cur_cate = cate_label[idx]
cur_score = cate_score[idx]
label_text = class_names[cur_cate]
#label_text += '|{:.02f}'.format(cur_score)
center_y, center_x = ndimage.measurements.center_of_mass(cur_mask)
vis_pos = (max(int(center_x) - 10, 0), int(center_y))
cv2.putText(img_show, label_text, vis_pos,
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.3, (255, 255, 255)) # green
if out_file is None:
return img
else:
back_ground = ~np.sum(seg_label,axis=0).astype(np.bool) #Gave the opposite value of segmentation
img_show[back_ground] = img[back_ground]*0+ color_mask * 0 #Multiplied the background by zero to remove the background
mmcv.imwrite(img_show, out_file)
accessed and modified inference.py of Solo code
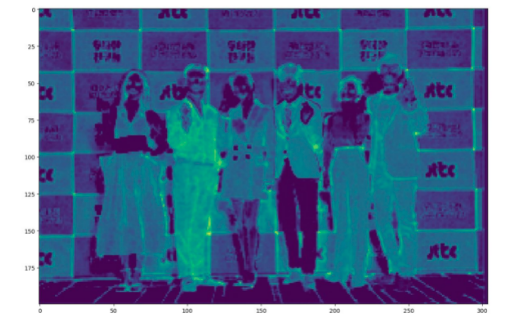
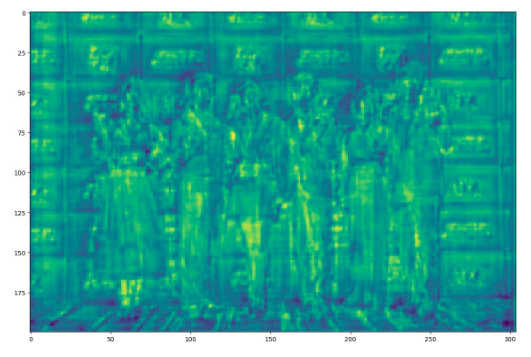
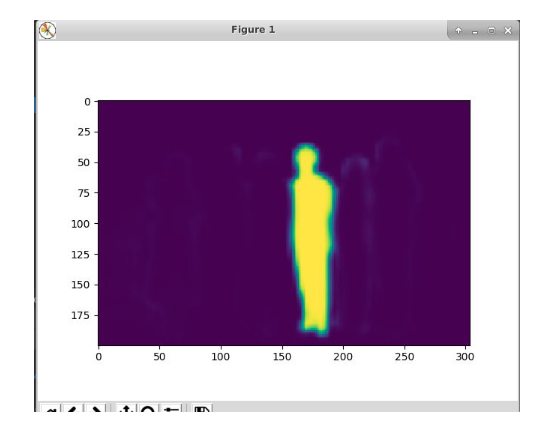
Figure 5. In the backbone network, the feature map is extracted through the resnet
-
Result



Figure 6. On the left, Original image. Middle, Image with one-shot instance segmentation. Right, image with data augmentation from my code.